What is stem cell regenerative therapy?
We have prepared two videos for those who are learning about stem cell regenerative therapy. If you are wondering “What is stem cell regenerative therapy?”, please watch the video.
4 minute overview video
Learn more videos
\ For those who want to know more/
What is stem cell regenerative therapy?
Article text below
Good news. This is especially good news for those suffering from diabetes complications and stroke sequelae.
More and more people are being saved by regenerative medicine.
Speaking of regenerative medicine, many people are probably familiar with “iPS cells”. Regenerative therapy using iPS cells is one of the most promising treatments worldwide, but it has yet to be put to practical use.
However, did you know that you can now receive regenerative therapy using special cells called “mesenchymal stem cells” that already exist in your body?
In this article, we will introduce mesenchymal stem cell regenerative therapy in detail.
What is stem cell regenerative therapy?
Stem cell regenerative therapy is a regenerative therapy that uses “stem cells” that have the ability to repair and regenerate cells and tissues that have become unable to perform their original functions due to disease.
In recent years, we often see the term iPS cells as a “dream therapy,” but due to various problems such as risks and costs, full-scale practical use has not yet been achieved. not here.
However, at present, the most practical regenerative therapy with the lowest risk is “stem cell regenerative therapy”.
Symptoms & diseases for which stem cell regenerative therapy is effective
Stem cell regenerative therapy targets the following diseases:
Metabolic disease
- Renal dysfunction
- Kidney disease
- Gout
- Chronic renal failure
Brain & Nerve disease
- Ethambutol optic neuropathy
- Facial paralysis
- Cluster headache
- Autonomic imbalance
- Neurological sequelae
- Hearing loss
- Herniated disc
- Epilepsy
- Brain stem hemorrhage
- Brainstem attendance sequelae
- Cerebral infarction
- Stroke sequelae
- Cerebral hemorrhage
- Brain tumor
- Tinnitus
- Spinal stenosis
Cardiovascular disease
- Acute myocardial infarction
- Angina pectoris
- High blood pressure
- Arrhythmia
- Atrial septal defect
- Idiopathic atrial fibrillation
Neurodegenerative disease
- ALS
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Cerebral palsy
- Parkinson’s disease
- Neuropathy
Fire extinguisher disease
- Liver dysfunction
- Liver disease
- Reflux esophagitis
- Enteritis
- Constipation
- Chronic cholecystitis
- Pancreaticobiliary maljunction
Respiratory disease
- COPD
- Bronchiectasis
- Asthma
- Pulmonary suppuration
Immune disease
- Atopic
- Atopic dermatitis
- Alcoholic urticaria
- Allergic predisposition
- Sjogren’s syndrome
- Chemical sensitivity
Locomotive system & Trauma
- Ligamentous injury
- Muscle loss
- Lumbar spondylosis
- Lower back pain
- Cervical spinal canal stenosis
- Tuberculous spinal caries
Others
- Menopause
- Sarcoid dosil
- Postpartum depression
- Periodontal disease
- Prostatic hypertrophy
- Male menopause
- Wrist pain
- Basedow’s disease
- Behcet’s disease
- Glaucoma
Advantages and disadvantages of treatment
There are advantages and disadvantages.
Advantage 1: Less physical burden on the patient.
The advantage of stem cell regenerative therapy is that it places less of a burden on the patient. The reason for this is that we do not administer surgical treatments using scalpels or drugs that are likely to cause side effects to the body, such as anticancer drugs.
Advantage 2: Treatment time is short.
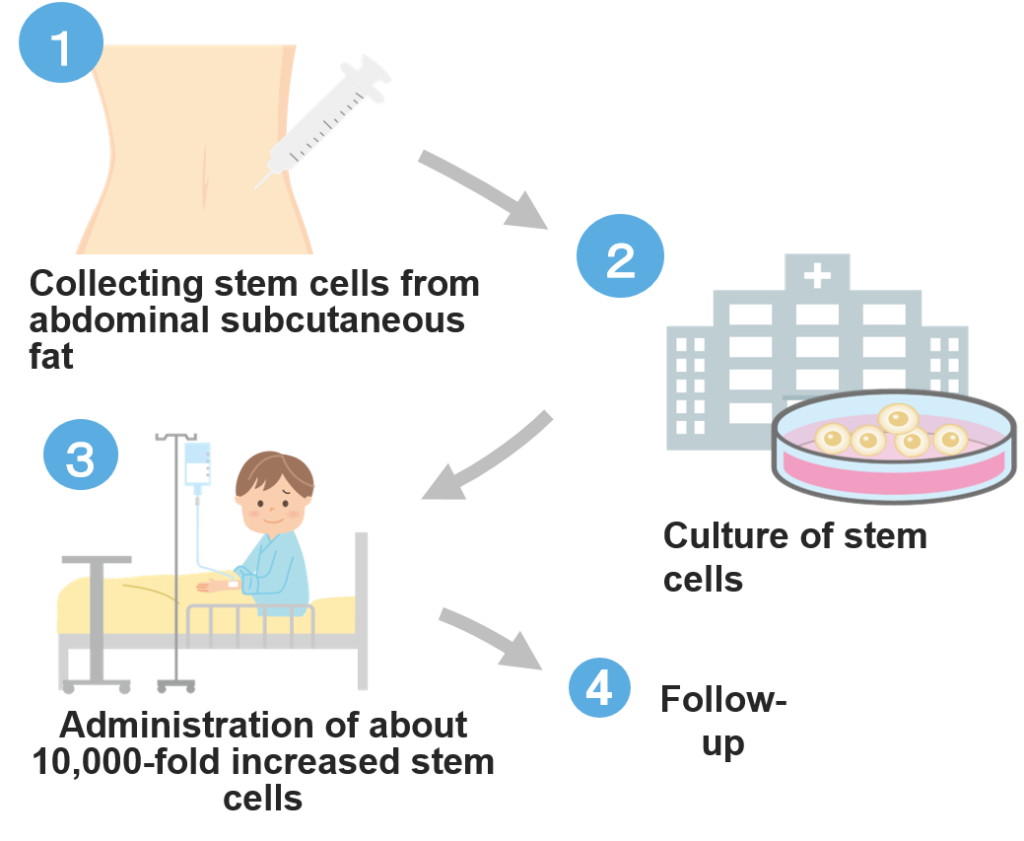
Another advantage of stem cell regeneration therapy is the short treatment time. The general flow of the actual treatment is (1) collecting stem cells from the patient’s body, (2) culturing the stem cells for a period of 4 to 6 weeks, and (3) increasing the number of stem cells. The flow is to return the stem cells to the patient’s body. Since (1) and (3) are performed with a syringe, the treatment is completed in a short time like an influenza vaccination.
Advantage 3: Less risk.
Stem cell regenerative therapy is a treatment that uses stem cells that exist in your own body. Therefore, it is characterized by low risk even in regenerative treatment. On the other hand, since iPS cells are artificially produced cells, they have the risk of becoming cancerous, and have not been put into full-scale practical use.
Disadvantage 1: Not covered by insurance.
Of course, stem cell regenerative therapy also has disadvantages. One of them is that it is not covered by insurance. Because insurance does not apply, the burden of treatment costs increases. However, due to advances in medical technology and the efforts of research institutes, hospitals, and companies, there is a movement to reduce treatment costs.
Disadvantage 2: Effects vary from person to person.
There are individual differences in the effects of stem cell regeneration therapy. Just as there are individual differences in how the effects of any treatment or drug are perceived, the same can be said for stem cell regeneration therapy.
Disadvantage 3: Depending on the symptoms, treatment may not be available.
Stem cell regeneration therapy cannot be treated depending on the symptoms. Rather, there are cases where you can not expect the effect even if you receive it. For example, when performing artificial dialysis. Even if the cultured stem cells are returned to the body, there is a possibility that the stem cells will be removed by artificial dialysis.
Flow of treatment
In the stem cell regeneration treatment that we provide, we will proceed with the following treatment flow.
STEP1: Counseling and examination

First, you will have a consultation with your doctor. We will also provide accurate information about this treatment. and discuss treatment strategies. On top of that, we will check the suitability for treatment by performing a preliminary examination such as blood sampling. If there are no problems at that stage, we will move on to collecting fat containing stem cells.
STEP2: Fat collection

The fat that contains stem cells is harvested. When collecting, local anesthesia is performed, and the tissue is collected from the subcutaneous fat of the abdomen. The amount of fat to be collected is about 5 mg. After collection, you will be asked to go home after observing the progress for about an hour.
STEP3: Extraction and culture of stem cells

Stem cells are extracted from the collected adipose tissue and cultured for 4 to 6 weeks until the number increases approximately 10,000 times. Culture is performed under strict quality control at a cell culture processing facility approved by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. We also conduct a sterility test on stem cells to confirm that they are safe stem cells.
STEP4: Administration of stem cells

On the day, a doctor will check your health condition, and if there are no problems, we will administer stem cells that have been cultured about 10,000 times. Administration of cultured stem cells is by intravenous infusion. After the end of the infusion, you will be asked to go home after about 1 hour of follow-up observation.
STEP5: Follow-up

Even after stem cell administration, regular medical examinations are performed to check the health condition in the long term. If it is difficult for you to visit the hospital regularly, we may contact you regularly to monitor your progress, or we may share your progress in cooperation with your family doctor.
The above is the basic content of stem cell regenerative therapy. In the next chapter, why is stem cell regenerative therapy used for diseases and symptoms in the first place? I will explain the mechanism of stem cell regenerative therapy.
Mechanism of stem cell regenerative therapy
Even if a gecko’s hand is cut off, it grows back. Did you know that geckos have amazing regenerative abilities?

In fact, recent research has shown that humans also have this ability to regenerate. As a result, stem cell regenerative therapy has come to be used as a treatment method by enhancing the human regenerative ability, that is, the self-repair function.
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are cells that have the ability to repair and regenerate cells and tissues that have lost their original functions due to disease. The reason why human babies grow so quickly is because they have a large amount of stem cells. We, humans, use a large amount of stem cells to enlarge and repair organs such as blood vessels, bones, and organs as we age.

However, the number of stem cells also decreases with age. For example, if the number of stem cells in a newborn is 100%, it is said that only 1/200 of that remains in people in their 80s.
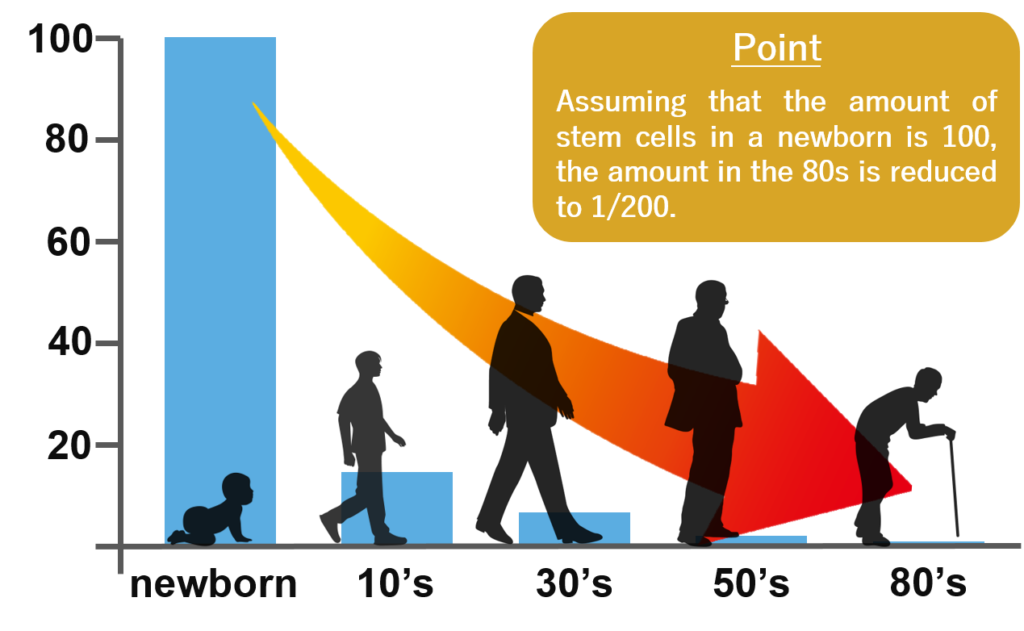
This is where stem cell regenerative therapy emerges, which attempts to regain the ability to repair and regenerate by administering a large amount of stem cells.
Differences from ES cells and iPS cells
By the way, when we talk about regenerative therapy, we often hear the terms “ES cells” and “iPS cells”, but what is the difference between such cells and stem cells?
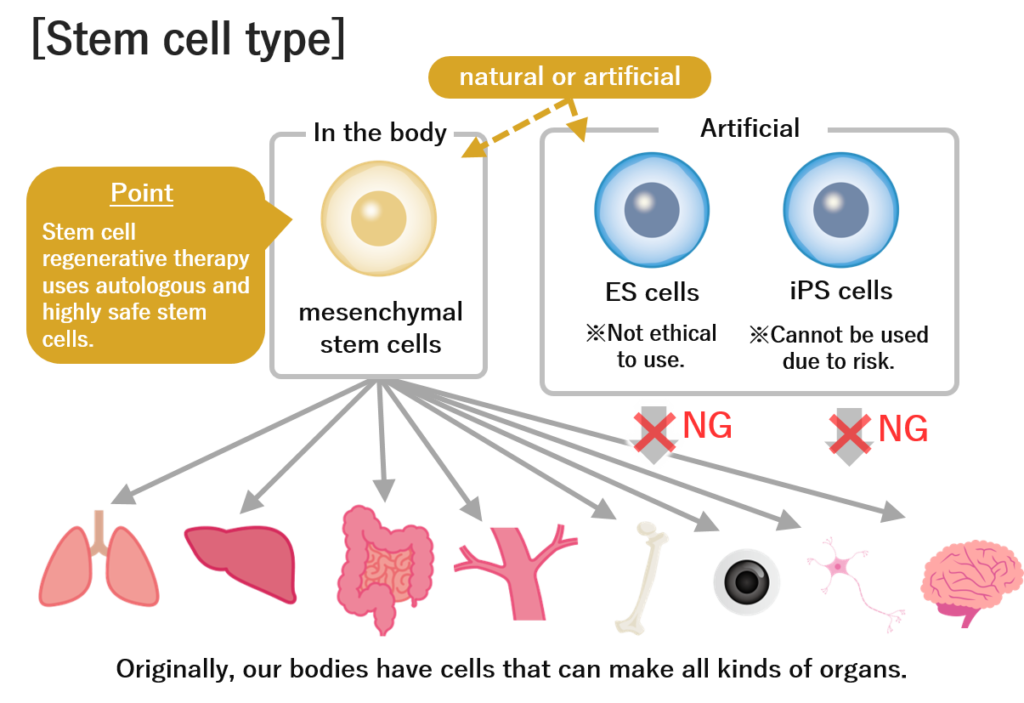
In fact, both ES cells and iPS cells are types of stem cells. However, those cells are artificially made stem cells.
Treatment using ES cells and iPS cells has been put into practical use in many countries other than Japan. However, in Japan, based on the “Regenerative Medicine Safety Law”, which was created only in Japan in 2014, the above two cells are classified as the first type with the highest risk. Therefore, it is still being researched at the clinical trial level and has not yet been put to practical use in general medical settings in Japan.
What are iPS cells?
iPS cells are stem cells that are artificially created from skin cells. And because it is an artificial stem cell, the risk is also a concern, and research at the clinical trial level is continuing. Therefore, wonderful research results are being reported day and night, and there is no doubt that it is a field that is expected to be developed as a dream-like therapeutic drug in the near future.
What are ES cells?
On the other hand, ES cells are artificial stem cells made from someone else’s fertilized egg. With the consent of the person undergoing fertility treatment, we use cells removed from unwanted embryos. However, in addition to the ethical issue of cells that could have become human, there is still the risk of immune reactions or rejection because they are cells of other people.
For the above reasons, it is currently difficult to receive regenerative therapy using artificial stem cells such as ES cells and iPS cells. Therefore, regenerative medicine using natural stem cells has emerged. In other words, it is possible to receive treatment using stem cells called mesenchymal stem cells, which are present in small amounts in our bodies.
Mesenchymal stem cells used for treatment
Despite the high expectations placed on ES cells and iPS cells, the reality is that there are still many problems.
Under such circumstances, it was found that the human body actually has a small number of natural stem cells called “mesenchymal stem cells”. Then, the few mesenchymal stem cells are taken out and cultured. Then, a treatment method was developed that can enhance the repair and regeneration ability by returning a large amount of mesenchymal stem cells back into the body.
This stem cell regeneration treatment uses the patient’s own mesenchymal stem cells. Therefore, it has less risk. Therefore, we recommend stem cell regenerative therapy using mesenchymal stem cells as a treatment method that has less risk and less burden on patients.
Safety of stem cell regenerative therapy
What about the safety of stem cell regenerative therapy? From here on, I will describe safety.
Stem cell regeneration therapy approved by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare
The stem cell regenerative therapy that we provide is classified in descending order of risk according to the number of cases and the degree of risk according to the Regenerative Medicine Safety Assurance Act, which came into force in Japan in November 2014. became. These are “Type 1 regenerative medicine, etc.”, “Type 2 regenerative medicine, etc.,” and “Type 3 regenerative therapy, etc.”.
Stem cell regenerative therapy is classified as type 2. In this way, in Japan, safety lines are established by law regarding regenerative treatment.
In the treatments we provide, stem cells are cultured at cell culture processing facilities approved by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare.
Beware of Stem Cell Regenerative Therapy Overseas
Stem cell regenerative therapy can be received overseas. However, there is no legal safety line. As a result, there is a possibility that imitation treatments or treatments with safety risks may be given.
For example, there are risky treatments such as injecting other people’s stem cells into the body or simply injecting water into the body, and even treatments that are fraudulent.
Therefore, we do not recommend overseas treatment. We recommend that you receive regenerative treatment in a medical environment such as ours, which is established according to Japanese law.
For those interested in stem cell regenerative therapy
At our company, for those who are interested in stem cell regenerative treatment but do not know what to do, we have set up free counseling that provides information, treatment consultation, and hospital information.
Guidance of the consultation window
We offer free counseling. If you are interested, please contact us by email or phone.

